Politics
INEC Chairman, Prof. Mahmood Yakubu and members of the Commission, meet with Media Organizations at the ongoing quarterly consultative meeting in Abuja, ahead of the 2024 Edo and Ondo States Governorship Elections on Wednesday, May 15th, 2024.

The President of the Nigeria Union of Journalists
President and Council Members of the NIPR
Senior Officials of the Nigerian Guild of Editors
Executive Director of the International Press Centre (IPC)
Media Executives and Heads of Various Media Organisations
Editors and Senior Journalists
National Commissioners of INEC
The Secretary and Other Senior Officials of the Commission
Members of the INEC Press Corps
Ladies and Gentlemen
1. It is my pleasure to welcome you all to our second regular quarterly consultative meeting for this year. You may recall that our first meeting for the year was held about two months ago on Thursday 21st March 2024 at which we briefed you about the 9 bye-elections and 38 re-run elections in 26 States of the Federation held on 3rd February 2024. We would like to further inform you that with the exception of two State Assembly constituencies in Enugu and Kano States disrupted by violence and thuggery, winners have emerged in 45 out of 47 constituencies. Following extensive consultation with stakeholders in the two States, the Commission is remobilising to conclude the outstanding re-run elections in Enugu South 1 State Constituency of Enugu State and Ghari (formerly known as Kunchi Local Government Area) for the Ghari/Tsanyawa State Constituency of Kano State. We similarly briefed you on the forthcoming off-cycle Governorship elections in Edo and Ondo States.
2. Early this week, the Commission announced the plan to resume the Continuous Voter Registration (CVR) as part of our preparations for the Edo and Ondo State Governorship elections. As you are aware, the Edo State Governorship election is holding in the next four months on Saturday 21st September 2024 while the Ondo Governorship election holds in the next six months on Saturday 16th November 2024.
3. The Continuous Voter Registration (CVR) in the two States will enable eligible citizens who are not registered voters to do so. Similarly, registered voters also have the opportunity to transfer their registration from other States of the Federation to Edo and Ondo States or from one location to another within the States. Lost or damaged voters’ cards will be replaced during the exercise. The CVR will take place simultaneously in the two States from Monday 27th May 2024 to Wednesday 5th June 2024 from 9.00am to 3.00pm daily including the weekend. Let me reiterate that the CVR is only open to new registrants and those who seek to transfer their registration. Persons who are registered as voters should not attempt to register again as double or multiple registration is illegal.
4. Taking into consideration the limited time to the Governorship elections, the Commission has decided to conduct the registration at Ward level and our State headquarters instead of our Local Government offices and a few designated centers as was the case in the past. This means that there will be 192 Ward registration centres in Edo State and 203 centres in Ondo State in addition to our State offices in Benin City and Akure, making a total of 397 walk-in registration centres in the two States. There will be no online pre-registration option in the two States because of time constraint. Each centre will be managed by two officials drawn from our regular staff and the National Youth Service Corps (NYSC). In the next few days, the Commission will commence the training of at least 794 officials for the exercise. The locations of the registration centres as well as other relevant information have been compiled in a detailed 28-page document included in your folders for this meeting. The same information has already been uploaded to our website and social media platforms for public information.
5. The Commission therefore appeals to the media to join us in mobilising prospective registrants for the exercise, particularly on the need to register early and not wait until the deadline approaches when the registration centres will be inundated by eleventh hour registrants.
6. In addition to the registration of voters, the Commission will also make available the uncollected Permanent Voters’ Cards (PVCs) for collection during the CVR. In the coming days, the list of uncollected PVCs will be published in our offices in the two States and simultaneously uploaded to our website. We believe that doing so will make it easier for voters to know the availability of the cards and identify the locations to collect them. However, no PVCs will be collected by proxy. Registered voters should come in person to collect their cards. Again, we seek for the support of the media in encouraging voters to locate and pick up thier PVCs as was done in the past.
7. Still on our preparations for the two Governorship elections, the Commission has published the final list of candidates for Edo following the conclusion of party primaries and the end of the period for withdrawal and substitution of candidates as provided in the Timetable and Schedule of Activities for the election. Campaign in public by political parties commenced on Wednesday 24th April 2024 and will end at midnight on Thursday 19th September 2024 i.e. 24 hours before the date fixed for the election as provided by law. We look forward reading your monitoring reports of the campaigns as some of you have done in the past.
8. As we move closer to Election Day in Edo State, it is also imperative to request media organisations to submit applications for accreditation to report on the election in earnest along with the required documentation for individual journalists and support staff. Doing so will enable the Commission to produce and deliver the identity cards for journalists covering the election in good time. The Commission will not entertain requests outside the deadline for the receipt of applications from interested media organisations or process requests that do not meet the criteria for accreditation.
9. Turning to outstanding bye-elections, the Commission would like to inform you about the existence of vacancies in four States of the Federation involving three State Assembly constituencies and one Federal Constituency as a result of death or resignation of Honourable Members. As soon as preparations are concluded, the Commission will announce the dates for bye-elections in Khana 2 State Constituency of Rivers State, the Bagwai/Shanono State constituency of Kano State, the Zaria Kewaye State Constituency of Kaduna State and the Garki/Babura Federal Constituency of Jigawa State.
10. On this note, I once again welcome you all to this meeting. I thank you and God bless.
Politics
Electoral Reform: Dino alleges senate’s plot to rig 2027 election
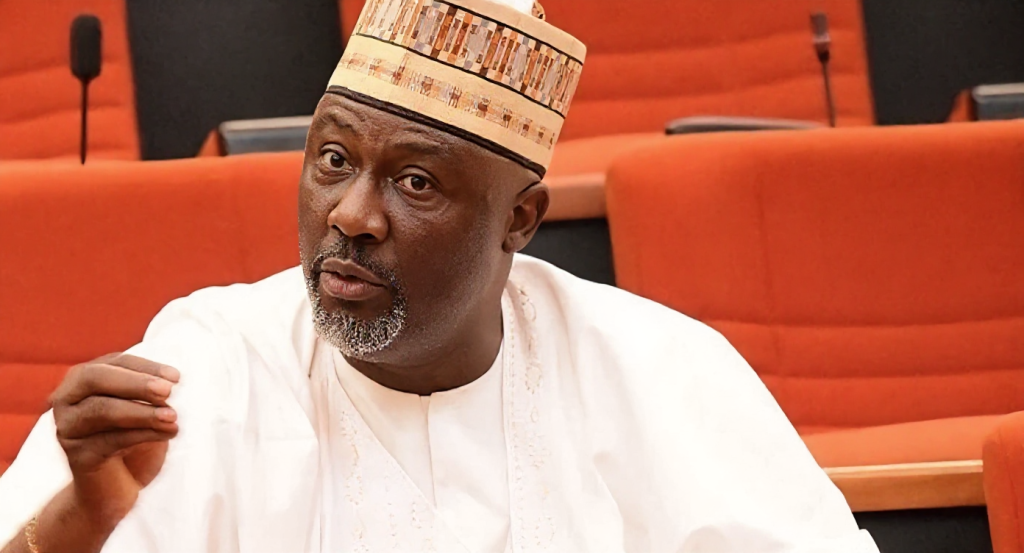
Former lawmaker, Dino Melaye Esq, has raised concerns over the Senate’s reported rejection of the electronic transmission of election results.
The move, according to Melaye, is a clear endorsement of election rigging and an indication of a sinister plan to rig the 2027 elections.
In a statement on Friday, the former lawmaker criticized the Senate’s decision, stating that it undermines the credibility of the electoral process.
The African Democratic Congress, ADC chieftain, also stated that the move opens the door for electoral manipulation and fraud.
He further warned that the rejection of electronic transmission of results is a step backwards for democracy in Nigeria.
Melaye called on lawmakers and citizens to stand up against “this blatant attempt to undermine the will of the people and ensure that future elections are free, fair, and transparent”.
Politics
Electoral Act: Nigerians have every reason to be mad at Senate – Ezekwesili

Former Minister of Education, Oby Ezekwesili, has said Nigerians have every reason to be mad at the Senate over the ongoing debate on e-transmission of election results.
Ezekwesili made this known on Friday when she featured in an interview on Arise Television’s ‘Morning Show’ monitored by DAILY POST.
DAILY POST reports that the Senate on Wednesday turned down a proposed change to Clause 60, Subsection 3, of the Electoral Amendment Bill that aimed to compel the electronic transmission of election results.
Reacting to the matter, Ezekwesili said, “The fundamental issue with the review of the Electoral Act is that the Senate retained the INEC 2022 Act, Section 60 Sub 5.
“This section became infamous for the loophole it provided INEC, causing Nigerians to lose trust. Since the law established that it wasn’t mandatory for INEC to transmit electoral results in real-time, there wasn’t much anyone could say.
“Citizens embraced the opportunity to reform the INEC Act, aiming to address ambiguity and discretionary opportunities for INEC. Yet, the Senate handled it with a “let sleeping dogs lie” approach. The citizens have every reason to be as outraged as they currently are.”
Politics
Electoral act: Senate’s action confirms Nigeria ‘fantastically corrupt’, ‘disgraced’ – Peter Obi

Former Labour Party presidential candidate, Peter Obi, has condemned the Senate’s refusal to make electronic transmission of election results mandatory, saying the move further exposes Nigeria as a fantastically corrupt and disgraced country.
Obi expressed his views in a statement shared on X on Friday, where he accused lawmakers of deliberately weakening Nigeria’s democratic process ahead of the 2027 general elections.
He explained that his reaction came after a brief pause to mourn victims of a deadly tragedy in Kwara State, where over 150 people reportedly lost their lives.
“Let us first pray for the souls of the innocent Nigerians lost in Kwara. That painful incident is why I delayed responding to the shameful development surrounding our electoral system,” he wrote.
Describing the Senate’s decision as intentional and dangerous, Obi said rejecting mandatory electronic transmission was not a simple oversight but a calculated attempt to block transparency.
“The Senate’s open rejection of electronic transmission of results is an unforgivable act of electoral manipulation ahead of 2027,” he said.
According to him, the action strikes at the heart of democracy and raises serious questions about the true purpose of governance in Nigeria.
“This failure to pass a clear safeguard is a direct attack on our democracy. By refusing these transparency measures, the foundation of credible elections is being destroyed. One must ask whether government exists to ensure justice and order or to deliberately create chaos for the benefit of a few.”
The former Anambra State governor linked the post-election controversies of the 2023 general elections to the failure to fully deploy electronic transmission of results, insisting that Nigerians were misled with claims of technical failures.
“
The confusion, disputes and manipulation that followed the 2023 elections were largely due to the refusal to fully implement electronic transmission,” he said.
He added that the so-called system glitch never truly existed.
Obi compared Nigeria’s electoral process with those of other African countries that have embraced technology to improve credibility, lamenting that Nigeria continues to fall behind.
“Many African nations now use electronic transmission to strengthen their democracy. Yet Nigeria, which calls itself the giant of Africa, is moving backwards and dragging the continent along.”
He criticised Nigeria’s leadership class, saying the country’s problems persist not because of a lack of ideas but because of deliberate resistance to meaningful reform.
“We keep organising conferences and writing policy papers about Nigeria’s challenges. But the truth is that the leaders and elite are the real problem. Our refusal to change is pushing the nation backwards into a primitive system of governance.”
Warning of the dangers ahead, Obi said rejecting electronic transmission creates room for confusion and disorder that only serves the interests of a small group.
He also recalled past remarks by foreign leaders who described Nigeria as corrupt, arguing that actions like this continue to justify those statements.
“When a former UK Prime Minister described Nigeria as ‘fantastically corrupt,’ we were offended. When former US President Donald Trump called us a ‘disgraced nation,’ we were angry. But our continued resistance to transparency keeps proving them right.”
Obi warned that Nigerians should not accept a repeat of the electoral irregularities witnessed in 2023.
“Let there be no mistake. The criminality seen in 2023 must not be tolerated in 2027.”
He urged citizens to be ready to defend democracy through lawful and decisive means, while also calling on the international community to closely monitor developments in Nigeria’s electoral process.
“The international community must pay attention to the groundwork being laid for future electoral manipulation, which threatens our democracy and development,” Obi stated.
He concluded by expressing hope that change is still possible if Nigerians take collective responsibility.
“A new Nigeria is possible but only if we all rise and fight for it.”
-
Business1 year ago
US court acquits Air Peace boss, slams Mayfield $4000 fine
-

 Trending1 year ago
Trending1 year agoNYA demands release of ‘abducted’ Imo chairman, preaches good governance
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoMexico’s new president causes concern just weeks before the US elections
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoPutin invites 20 world leaders
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoRussia bans imports of agro-products from Kazakhstan after refusal to join BRICS
-
Entertainment1 year ago
Bobrisky falls ill in police custody, rushed to hospital
-
Entertainment1 year ago
Bobrisky transferred from Immigration to FCID, spends night behind bars
-
Education1 year ago
GOVERNOR FUBARA APPOINTS COUNCIL MEMBERS FOR KEN SARO-WIWA POLYTECHNIC BORI













