Tech
Top secret lab is developing the UK’s first quantum clock

- READ MORE: Google’s quantum chip can perform ‘impossible’ tasks in five mins
A top secret lab is developing a super-precise ‘quantum clock’ that could revolutionize British intelligence.
This super-accurate timekeeping device, to be rolled out by 2029, will allow more precise navigation and surveillance on Royal Navy ships and RAF planes.
It will also ‘enhance the accuracy of advanced weapons’ like guided missiles and give British computer boffins the edge over online adversaries like cyber criminals.
The clock’s precision will be so refined that it will lose less than one second over billions of years, allowing scientists to measure time at an unprecedented scale.
It is the first device of its kind to be built in the UK and will be deployable on military operations in the next five years, according to Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (DSTL).
‘This first trial of advanced atomic clock represents a significant achievement in the UK’s quantum technology capabilities,’ said DSTL chief executive Paul Hollinshead.
‘The data gathered will not only shape future defence effort but is also a signal to industry and academia that we are serious about exploring quantum technologies for secure and resilient operational advantage.’
Quantum clocks use quantum mechanics – the physics of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic scale – to keep time with unprecedented accuracy by measuring energy fluctuations within atoms.

Developed at the top-secret Defence Science and Technology Laboratory, (Dstl) the quantum clock will improve British intelligence and surveillance by decreasing the reliance on GPS technology, which can be disrupted and blocked by adversaries

To be rolled out by 2029, the quantum clock will allow more precise navigation and surveillance on Royal Navy ships and RAF planes. Pictured, Royal Navy Duke class Type 23 anti-submarine frigate HMS Portland
Quantum clocks are even more accurate that the ‘atomic clocks’, of which there are approximately 400 already in operation around the world.
The UK already has an atomic clock at the National Physical Laboratory in London, but this quantum clock will be the country’s first.
Nick France, CTO of Sectigo, told MailOnline: ‘A quantum clock is a type of atomic clock – essentially a super-accurate timekeeping device.
‘Atomic clocks work by measuring the resonant frequency of atoms, whereas quantum clocks measure very small energy changes (‘quantum fluctuations’) in these atoms, leading to increased accuracy even over super-accurate atomic clocks.
‘Atomic clocks currently are incredibly accurate anyway, but a quantum clock has accuracy levels where only a single second is lost in billions of years of operation.’
The British quantum clock will be ‘the first device of its kind to be built in the UK’, said the UK government in a statement, but it will not be a world first.
Back in 2010, the University of Colorado at Boulder developed a quantum clock with the US National Institute of Standards and Technology.
However, key barriers to deploying quantum clocks are their size – current models come in a van or in a car trailer and are about 1,500 litres in volume.

Atomic clocks use certain resonance frequencies of atoms to keep time with extreme accuracy. Pictured, atomic clock at the University of Colorado Boulder in the US
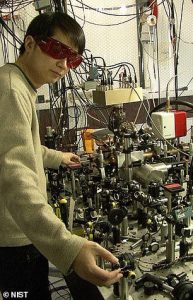
Back in 2010, the University of Colorado at Boulder developed a quantum clock with the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (pictured)

Pictured, NIST-F1, source of the official time of the USA
Just like most quantum equipment, quantum also have sensitivity to environmental factors such as heat and air molecules, limiting their transport between different places.
‘Quantum clocks are not small like watches or alarm clocks,’ France added.
‘These are devices that in current implementations can be large, even room-sized devices.
‘However, improvements in technology will decrease the size of these devices making them more portable.’
Apart from just ultra-precise timekeeping, quantum clocks could transform global navigation systems by helping satellite communications and aircraft navigation.
According to DSTL, their quantum clock will enable more precise and independent navigation systems, reducing reliance on GPS satellites, which are vulnerable to jamming or destruction in conflict scenarios.
It will improve communications systems, such as encrypted military networks, which depend on highly synchronised timekeeping, as well as boosting the accuracy of advanced weapon systems like guided missiles, which rely on accurate timing to calculate trajectories and coordinate attacks.
What’s more, British Armed Forces will get an edge over adversaries in ‘timing-critical operations’, such as cyber warfare, where milliseconds can make a difference.

Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is defined by sophisticated, ultra-precise ‘atomic clocks’ around the world, which tick precisely and continuously. Experts are pictured here with the NIST-F2 atomic clock in the US
Cyber warfare refers to the actions by a nation-state or international organization to attack and attempt to damage another nation’s computers or information networks.
France told MailOnline: ‘Super-accurate timekeeping is important to governments and militaries to enable accurate navigation (using GPS or similar technologies) of planes and ships, but also guidance of weapons systems such as missiles.
‘Equally important to the military as well as civilians is secure communications.
‘Much of the secure communications for governments and the military relies on accurate time sources to function.
‘But equally these accurate clocks are useful for more civilian applications and general internet security, even securing your personal data as it’s transmitted around the internet.’
Companies and governments around the world are keen to cash in on the huge potential benefits that the spooky effects of quantum technology could bring.
Google last month unveiled a new quantum computing chip it said could do in minutes what it would take leading supercomputers 10 septillion years to complete.
Eventually, such a chip could power a ‘commercial’ quantum computer that could be purchased by members of the public and used in labs, offices and even homes.
These ultra-powerful machines, which use the spooky effects of quantum physics, could do everything from speed up AI, solve climate changeand discover lifesaving drugs.
Tech
Google acquires energy company Intersect for $4.75 billion

Google is acquiring energy infrastructure company ‘Intersect’ for $4.75 billion (approximately 7 trillion Korean won) to secure the power needed for its AI (artificial intelligence) data centers. The move aims to address the power issue, the biggest hurdle in expanding data centers. Google, which developed the ‘Gemini’ AI, is a so-called ‘AI full-stack’ company equipped with all AI-related technologies and services, including AI chips and cloud (virtual servers). The strategy is to directly manage the energy infrastructure needed to actually operate AI as well.
Reuters reported on the 22nd (local time) that Google is acquiring Intersect for $4.75 billion in cash. Google already holds a minority stake in Intersect, and through this acquisition, it will also secure the gigawatt (GW)-level energy and data center projects that Intersect is developing and constructing. Intersect is expected to be responsible for building Google’s data center power infrastructure in the U.S., based on its technology linking power generation facilities and power grids.
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google and Alphabet, said, “Intersect will enable us to build power infrastructure more quickly and flexibly in line with the increasing demand for AI data centers,” adding, “It will also be an important partner in strengthening America’s energy innovation and technological leadership.”
Bloomberg reported that Intersect’s energy assets currently in operation or under construction in the U.S. amount to $15 billion (approximately 22.2 trillion Korean won).
◇Google increasing energy investments
Google has recently been increasing its investments in the energy sector. Although the company possesses AI chips (TPUs), Gemini, and search and cloud services, stable energy supply is essential to support these businesses.
To this end, Google is also investing in nuclear power technology. In October of last year, it signed a long-term cooperation agreement with small modular reactor (SMR) startup ‘Kairos Power’ to secure up to 500 MW (megawatts) of power. It is noted as the first case among big tech companies to publicly declare securing SMR-based power. Additionally, in August, Google and Kairos Power announced plans to build the next-generation SMR ‘Hermes 2’ in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. The goal is to commence operation in 2030.
Google is also restarting previously shut-down nuclear power plants to secure energy. In October, it announced that it will collaborate with ‘NextEra Energy’ to restart the Duane Arnold Nuclear Generating Station in Iowa, which was closed in 2020. The target restart period is between 2028 and 2029.
Google is also investing in renewable energy such as geothermal power. Since 2023, it has been supplying power to data centers through geothermal power generation with ‘Fervo Energy’ in Nevada, U.S.
Google is also actively investing in next-generation energy technologies that are not yet commercialized. In 2022, it made a large-scale investment in ‘TAE Technologies,’ which possesses nuclear fusion technology. Nuclear fusion power generation is a technology that applies the principle of energy creation in the sun, combining atomic nuclei to produce energy. It is called the ‘dream energy’ because it has abundant fuel resources, emits no carbon, and, unlike conventional nuclear power plants, does not produce high-level nuclear waste. However, it is assessed that more time is needed for commercialization due to technical challenges. Recently, TAE Technologies has accelerated the commercialization of fusion energy by merging with Trump Media Group (TMTG).
Tech
“I Lost $1.2 Million To Hackers On One Of My Apps. I Caught One Of The Hackers, And Instead Of Handing Him Over To The Police, I Employed Him To Work For Me.”- BLord

Anambra Born tech entrepreneur and businessman Linus Williams, popularly known as BLord, has shared an unusual story about how he handled a major cyberattack on one of his applications.
According to BLord, he lost $1.2 million to hackers who infiltrated one of his digital platforms. In the course of tracking the incident, he successfully identified one of the individuals involved in the breach.
Rather than handing the suspect over to security agencies, BLord said he made a strategic decision: he employed the hacker.
He explained that the hacker’s skills, though misapplied, were exceptional and could be redirected towards strengthening his company’s cybersecurity systems.
BLord noted that the decision was driven by a desire to turn a negative experience into an opportunity for growth and to better secure his business infrastructure.
Tech
MAN Honours Zobis Cable CEO, Ezeobi, at 37th AGM
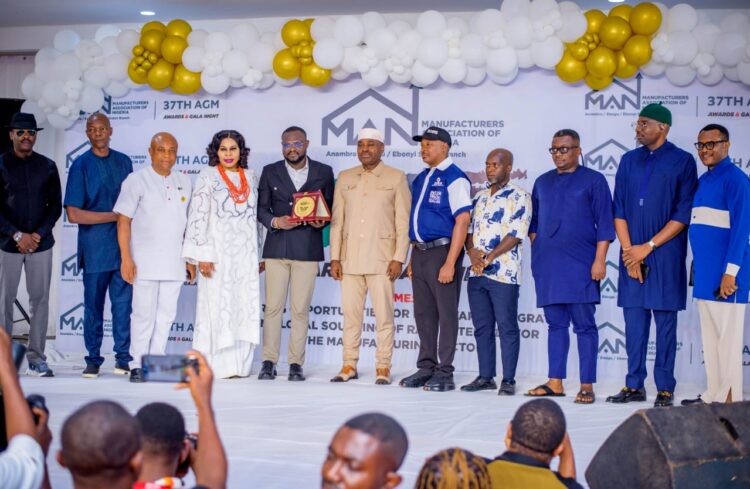

The MD/CEO of John Zobis Group, Mr. John Ezeobi, has again been honoured with another major industry prize in recognition of his contributions to local sourcing, innovation and the growth of Nigeria’s manufacturing capacity.
The prestigious award, “Pillar of Industrial Enterprise and National Impact,” which was conferred on him by the Manufacturers Association of Nigeria (MAN) — Anambra, Ebonyi and Enugu Zone, was presented during the association’s 37th Annual General Meeting, Awards & Gala Night at the International Conference Centre, Enugu.
coming barely three weeks after Ezeobi was nominated as the winner of The Sun’s Industrialist of the Year Award 2025 by the Management of The Sun Newspaper, a run of recognition that has further highlighted his rising profile in the South-East manufacturing ecosystem.
The latest award, it was gathered, celebrates Ezeobi’s deliberate investment in backward integration, his push for local sourcing of raw materials and efforts to strengthen domestic value chains, which MAN described as essential to reducing import dependence and creating jobs across the region.
Chaired by Chief Obinna Iyiegbu (Obi Cubana), the well-attended occasion, themed “Exploring Opportunities for Backward Integration and Local Sourcing of Raw Materials for the Manufacturing Sector,” brought together regulators, policymakers, manufacturers and industry stakeholders and also featured presentations, panel sessions and cultural performances, among other highlights.
Speaking at the event, the Keynote Speaker and Director-General of the Raw Materials Research and Development Council (RMRDC), Prof. Nnanyelugo Ike-Muonso, said the economic benefits of exploring Opportunities for backward integration and local sourcing of raw materials for the Manufacturing sector cannot be overemphasized.
Prof. Ike-Muonso told delegates that Nigeria spent over ₦3.53 trillion importing raw materials in the first half of 2025 alone, warning that such dependence continues to weaken the nation’s economy. He further argued that the proposed 30% Value Addition Bill, which would require a minimum local value addition before export, would be transformational if signed into law.
He also outlined the bill’s potential to expand GDP, generate hundreds of thousands of jobs and save foreign exchange by keeping more of the country’s raw-material wealth in domestic supply chains, boost local manufacturing, and generally reposition Nigeria as a regional industrial hub.
On his own part, the Governor of Enugu State, Dr. Peter Mbah, endorsed the call for stronger industry-academia partnerships and urged financial institutions to make affordable credit available to manufacturers who adopt backward integration. The governor, who was represented by his Deputy, Barrister Ifeanyi Ossai, described the policy pathway as key to moving Nigeria from resource export dependence toward higher-value industrial output.
Reacting via his social handle shortly after receiving the award, the Zobis Cable Boss expressed gratitude for the honour, describing it as a strong motivation to do more in driving local production, reducing import dependence, and strengthening Nigeria’s industrial base.
Ezeobi, who received the plaque from pioneer Nollywood star and legal practitioner, Barr. Kenneth Okonkwo, attested that the AGM provided a critical platform for renewed commitment to backward integration as a pathway to sustainable industrial development.
“The event highlighted the critical importance of backward integration and local sourcing of raw materials as strategic levers for strengthening domestic production, reducing import dependency, and building resilient, self-sustaining industries. A meaningful platform for driving progress and collaboration across Nigeria’s manufacturing sector,” he partly wrote.
Also speaking, the Chairman of MAN for the Anambra-Ebonyi-Enugu zone, Dr. Adaora Chukwudozie, described local sourcing as the pragmatic route to lowering production costs and stabilizing supply chains for SMEs and larger manufacturers alike. She welcomed RMRDC’s roadmap and invited state governments to partner in establishing raw-material corridors and shared processing facilities that would bring inputs closer to factories.
The event, which had His Eminence, Eze Eberechukwu Orji, Eze Aro, as the Royal Father of the Day, was also graced by other notable dignitaries and stakeholders, which include Senator Osita Izunaso, Dr. Gideon Chidiebere Osi, Ichie Sunday Ezeobiora , Chairman, Sunchi Farms; Mr Linus Williams Ifejika, Chairman Blord Group; Otumba Francis Meshioye, National President, Manufacturers Association of Nigeria; Dr. Ifeanyi Okoye, Chairman, Juhel Pharmacy; Chief Dr. Dan Chukwudozie, Chairman,Dozzy Group; Dr. Chike Obidigbo,Chairman, Hardis and Dromedas; Anambra Commissioner for Trade and Industry,Mr. Christian Udechukwu.














-
Business1 year ago
US court acquits Air Peace boss, slams Mayfield $4000 fine
-

 Trending1 year ago
Trending1 year agoNYA demands release of ‘abducted’ Imo chairman, preaches good governance
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoMexico’s new president causes concern just weeks before the US elections
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoPutin invites 20 world leaders
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoRussia bans imports of agro-products from Kazakhstan after refusal to join BRICS
-
Entertainment1 year ago
Bobrisky falls ill in police custody, rushed to hospital
-
Entertainment1 year ago
Bobrisky transferred from Immigration to FCID, spends night behind bars
-
Education1 year ago
GOVERNOR FUBARA APPOINTS COUNCIL MEMBERS FOR KEN SARO-WIWA POLYTECHNIC BORI













