While robotic surgery is advancing rapidly, experts warn that medicine cannot function without human judgement, accountability and ethical responsibility.
Watch video below:
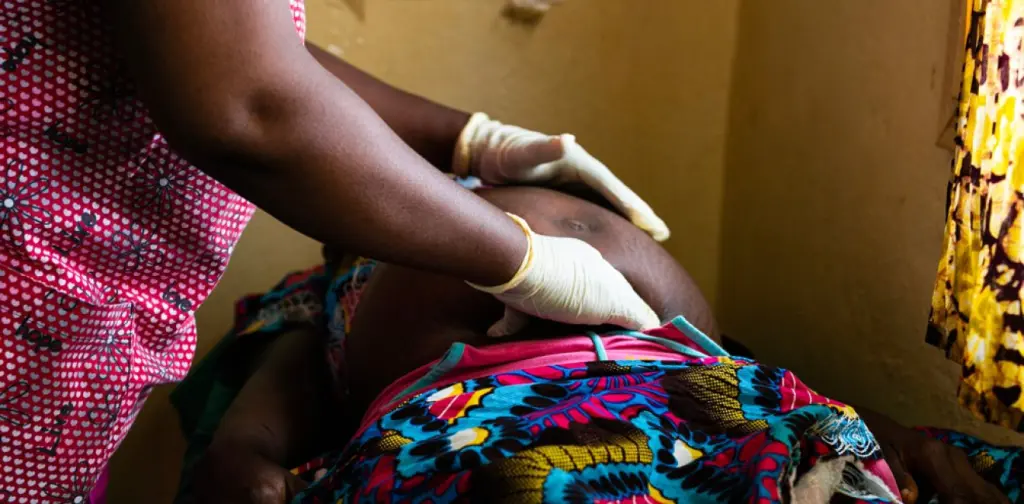
The World Health Organization (WHO) has raised concerns over the high rate of maternal deaths in Africa, with Nigeria among the most affected countries.
According to a newly released study, complications such as hemorrhage, severe bleeding, and hypertensive disorders, including preeclampsia, remain the leading causes of maternal deaths across the continent.
The report, published in The Lancet Global Health, revealed that in 2020 alone, an estimated 287,000 women worldwide died from pregnancy-related complications, with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for a significant portion of these deaths.
Nigeria, which has one of the highest maternal mortality rates globally, continues to face challenges in providing adequate healthcare for pregnant women, particularly in rural and underserved communities.
The WHO study found that excessive bleeding during or after childbirth was responsible for nearly one-third of maternal deaths, while hypertensive disorders, such as preeclampsia, accounted for an additional 16%. Other critical factors contributing to maternal deaths included infections, unsafe abortions, childbirth-related injuries, and a lack of access to emergency obstetric care.
Dr. Pascale Allotey, WHO’s Director of Sexual and Reproductive Health and Research, stressed that most of these deaths could be prevented with timely medical intervention and improved maternal healthcare services.
She highlighted the urgent need for African governments, including Nigeria, to strengthen key aspects of maternity care, such as antenatal services, skilled birth attendance, and emergency obstetric care.
In Nigeria, poor healthcare infrastructure, inadequate medical personnel, and financial constraints continue to limit access to essential maternal health services. Many women, particularly in rural areas, give birth at home without the assistance of trained healthcare providers, increasing the risk of complications and death. Additionally, a lack of awareness about preeclampsia and other pregnancy-related conditions often leads to delayed medical intervention.
Northern Nigeria continues to face one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the world, with thousands of women dying each year due to pregnancy-related complications.
The region, which accounts for a significant portion of Nigeria’s population, struggles with inadequate healthcare facilities, cultural barriers, poverty, and insecurity, all contributing to the high number of maternal deaths.
According to reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Nigeria Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS), Nigeria accounts for nearly 20 percent of global maternal deaths, with northern states experiencing the highest burden.
In states such as Kano, Sokoto, Zamfara, Jigawa, and Yobe, maternal mortality rates exceed 1,000 deaths per 100,000 live births, far above the national average of 512 deaths per 100,000 live births. Rural areas remain the most affected, with maternal deaths recorded at rates three to five times higher than in urban centers.
The leading causes of maternal deaths in the region include severe bleeding during childbirth, hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia, infections, unsafe abortions, and complications from prolonged labor. Many of these deaths occur due to poor access to quality healthcare, as rural communities often lack functional health facilities, skilled birth attendants, and emergency obstetric services. Often, women must travel long distances to reach hospitals, a delay that often proves fatal.
WHO’s findings emphasized the importance of postnatal care, noting that most maternal deaths occur during or shortly after childbirth. Yet, in many African countries, including Nigeria, a significant percentage of women do not receive follow-up care within the first few days after delivery. This gap in healthcare services increases the risk of complications that could otherwise be managed with timely intervention.
Dr. Jenny Cresswell, a WHO scientist and co-author of the study, pointed out that multiple interrelated factors contribute to maternal mortality in Africa. For instance, conditions like preeclampsia can increase the likelihood of severe bleeding and other life-threatening complications long after childbirth. She called for a holistic approach to maternal health, emphasizing that access to quality healthcare before, during, and after pregnancy is essential to saving lives.
In 2024, WHO and its partners launched a global roadmap to combat postpartum hemorrhage, one of the leading causes of maternal death. The initiative aims to improve access to lifesaving medical treatments, particularly in low-resource settings like Nigeria. Furthermore, the 194 member states of the World Health Assembly recently passed a resolution committing to strengthening maternal and newborn healthcare services.
As part of its ongoing efforts, WHO has announced that World Health Day 2025 will focus on maternal and newborn health, calling for a significant scale-up of healthcare services in the poorest and most crisis-affected regions. The campaign will not only emphasize reducing maternal deaths but also advocate for improved postnatal care, mental health support, and access to quality reproductive health services for African women.
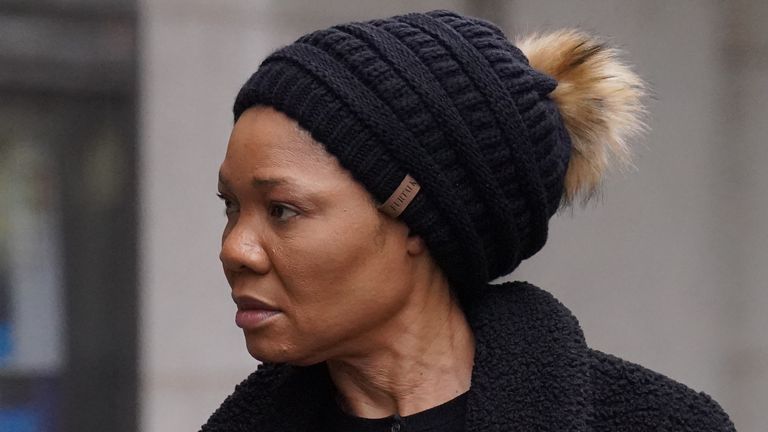

Wife of former Deputy Senate President Ekweremadu returns home following custodial sentence, while her husband remains imprisoned in UK.
The wife of former Nigerian Deputy Senate President, Ike Ekweremadu, Beatrice, has returned to Nigeria after being released from a prison in the United Kingdom.
Her arrival in the country on Tuesday, January 21, 2026, followed the completion of the custodial portion of her sentence for her role in a high-profile organ-harvesting conspiracy.
Mrs Ekweremadu was received by family members and close associates at the Nnamdi Azikiwe International Airport in Abuja, marking her first time on Nigerian soil since the legal saga began in mid-2022.
While her return has sparked celebrations in her hometown of Mpu, in the Aninri Local Government Area (LGA) of Enugu State, it came amid the continued incarceration of her husband in London.
The return of the former Deputy Senate President’s wife followed her May 2023 conviction by the Old Bailey in London.
She was sentenced to four years and six months in prison for conspiring to facilitate the travel of a 21-year-old Lagos Street trader to the UK for the purpose of harvesting his kidney.
The organ was intended for the couple’s daughter, Sonia, who suffered from a chronic kidney condition.
The case, which was prosecuted under the UK’s Modern Slavery Act 2015, marked the first time the legislation was used in a human organ-harvesting prosecution.
Under UK law, non-violent offenders are typically eligible for release on license after serving half of their custodial term.
Reports indicated that Mrs. Ekweremadu’s release was further facilitated by her good conduct record and by a broader UK government initiative to address severe prison overcrowding.
Despite his wife’s return, Senator Ekweremadu remains in a UK correctional facility serving a significantly longer sentence.
In May 2023, the former lawmaker was handed a nine-year and eight-month term, as the court deemed him the primary driver of the conspiracy.
Efforts by the Nigerian federal government to secure his release or repatriation have so far been unsuccessful.
In late 2025, a high-powered diplomatic delegation visited London to explore a Prisoner Transfer Agreement (PTA) that would allow the Senator to serve the remainder of his term in a Nigerian facility.
However, the UK Home Office reportedly rejected the proposal in November 2025, citing concerns over the guarantee of the sentence’s continued enforcement if transferred to the Nigerian jurisdiction.
The third convict in the case, Dr. Obinna Obeta, who was described by the prosecution as the medical “middleman,” continues to serve a 10-year prison sentence in the UK.
Meanwhile, the couple’s daughter, Sonia, who was cleared of all criminal charges during the 2023 trial, remains in the United Kingdom, where she is reportedly receiving ongoing medical treatment for her condition.

Elon Musk has asserted that medical degrees may soon become obsolete, as AI-powered robots are expected to surpass human surgeons in performance.
The Tesla and SpaceX CEO claimed that humanoid robots like Tesla’s Optimus will outperform the world’s best surgeons within three years.
Speaking on the Moonshots podcast hosted by Peter Diamandis, Musk argued that human doctors are slow to train, prone to error, and fundamentally limited.
“Right now there’s a shortage of doctors and great surgeons,” Musk said.
“[It takes] a super long time to learn how to be a good doctor Doctors have limited time, they make mistakes. How many great surgeons are there? Not that many,” he added.
“So don’t go to medical school?” Diamandis asked Musk.
While robotic surgery is advancing rapidly, experts warn that medicine cannot function without human judgement, accountability and ethical responsibility.
Watch video below:

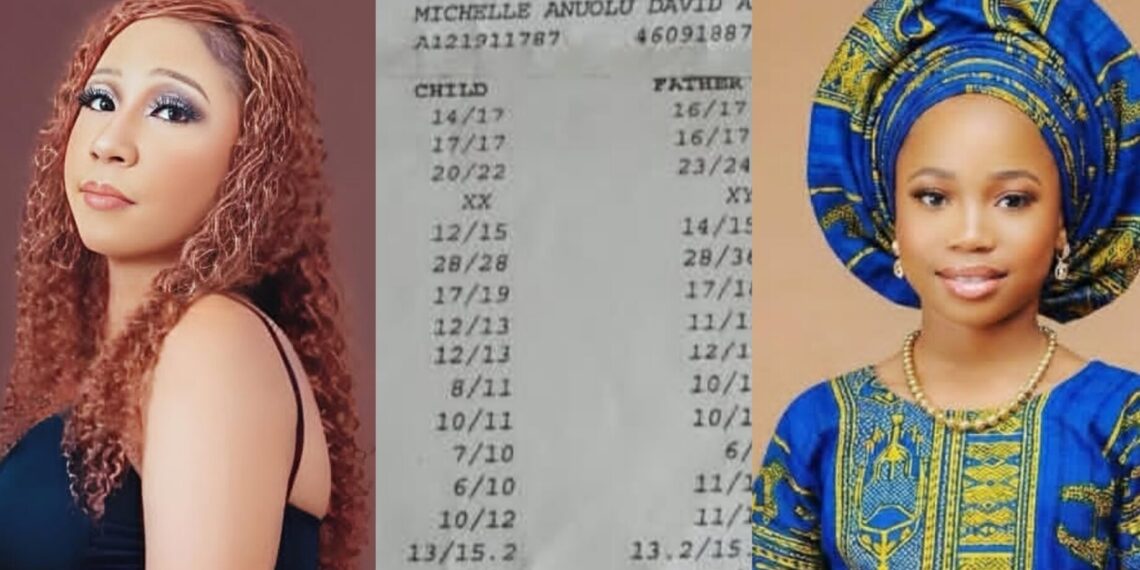
In a recent development, the ongoing controversy surrounding Ayo Labinjoh, the mother of Anu and Afrobeats superstar, Davido, over partenity dispute has intensified.
It’s worth noting that Ayo Labinjoh and Davido have been in the headlines over paternity dispute, with the singer claiming five DNA tests yielded negative results
In a fresh Instagram post, Ayo shared an existing DNA test result contradicting Davido’s earlier claim.
She emphasized that the DNA test result was valid, while investigative journalist, Kemi Olunloyo has fought vigorously for her daughter.
Her post reads,“The ONLY DNA 


Meanwhile, Davido has revealed that his father, Dr. Adedeji Adeleke, played a significant role amid his paternity dispute with Ayo Labinjoh.
In a recent tweet on X (formely Twitter), the ‘Feel’ crooner shared that his father insisted that he undergo DNA test.
“You guys don’t know my father..He’s even the one that forced me to go. Adeleke’s we don’t play about Blood on this side”, The tweet reads.
Meanwhile, Cubana Chief Priest’s alleged baby mama, Helen Atti, has weighed in on Davido’s paternity dispute.
She took to the singer’s comment section, writing, “Please just help her, you can still adopt her, it doesn’t mean anything. I know you love children a lot, not like Pascal Okechukwu, big belle for no reason”.
See below…..

US court acquits Air Peace boss, slams Mayfield $4000 fine


NYA demands release of ‘abducted’ Imo chairman, preaches good governance


Mexico’s new president causes concern just weeks before the US elections


Putin invites 20 world leaders


Russia bans imports of agro-products from Kazakhstan after refusal to join BRICS
Bobrisky falls ill in police custody, rushed to hospital
Bobrisky transferred from Immigration to FCID, spends night behind bars
GOVERNOR FUBARA APPOINTS COUNCIL MEMBERS FOR KEN SARO-WIWA POLYTECHNIC BORI